Further publications have been added to our Anti-EBNA2, clone PE2 datasheet, bringing the total number of citations to eight. PE2 was developed by Professor Martin Rowe in the late 80s at Birmingham University. Professor Rowe’s focus of research has been on the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) since the early 80s when he took up his first postdoctoral position with Professor Anthony Epstein in Bristol.
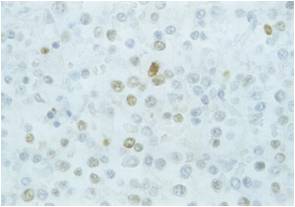
Immunohistochemical analysis of EBNA2 expression in post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder case 2 using PE2. Image taken from Brink et al. 1997. J Clin Pathol. 50(11):911-8.
EBV is an interesting member of the herpesvirus family. It has been primarily associated with infectious mononucleosis (glandular fever), a condition usually seen within adolescents. However as many of its family members, the EBV also has the capability of causing certain types of cancer such as Hodgkin's lymphoma, Burkitt's lymphoma and conditions associated with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Clone PE2 recognises the EBV encoded nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2), which acts as a transcriptional activator of cellular and viral genes and plays a crucial role in the immortalization of human primary B-cells by EBV. Currently antiviral treatments and immunological approaches have been used to treat EBV-associated tumours; however there are many limitations to these therapies. Therefore use of PE2 in a range of methods will hopefully enable us to further understand the role of EBNA2 in EBV associated tumours.

PE2 detects the 88 kDa EBNA2A protein in a Western Blot analysis. Image taken from Brink et al. 1997. J Clin Pathol. 50(11):911-8.
View the datasheet for more information and publications.
HAVE YOU REGISTERED?
Join the ever-growing global Ximbio community. Register and receive updates about new reagents, institutes and new features being added to the website.
