Anti-N6-methyladenosine (m6A), clone 17-3-4-1, is one of Ximbio’s newest products. Anti-m6A is a monoclonal antibody which recognises m6A in both modified RNA and DNA. Clone 17-3-4-1 was raised against hapten N6-methyladenosine-5’-monophosphate conjugated to BSA and has application in immunoprecipitation and dot blots.
m6A is the most prevalent internal modification present in the mRNA of all higher eukaryotes, as well as Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Although this modification has been shown to be essential for cell viability and development, its exact function still remains unknown.
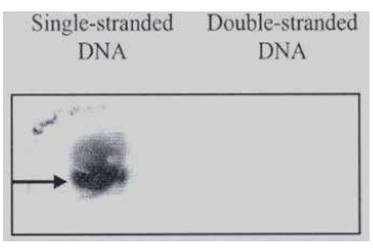
Southern analysis showing anti-m6A recognising single-stranded DNA. Arrow indicates the m6A containing fragment.
Anti-m6A was developed by Rupert Fray’s team at the University of Nottingham. It was produced in order to enable Rupert’s team to develop a new antibody based technique for identifying m6A containing messages. The team discovered that there is a substantial level of m6A modification in the GpA context in sporulating yeast and used the novel technique to identify some of the methylated transcripts. This finding highlighted the significance of m6A modifications as it is consistent with the preferred methylation consensus of higher eukaryotes and suggests conservation across distinct species.
Due to their prevalence and significance (especially in stem cell differentiation) m6A modifications in mRNA have attracted a wealth of interest. They have been published upon extensively in high profile journals and studied in a variety of model organisms including human, mouse, plant and Drosophila.
In addition, similar antibody based approaches indicate that DNA of Drosophila (Chen et al.) and C.elegans (Shi et al.) may also be a target of dynamic m6A methylation and de-methylation.
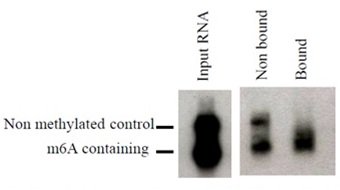
Clone 17-3-4-1 can be used to purify synthetic methylated transcripts. Radiolabelled control non-methylated (350 nt) and methylated (250 nt) input transcripts can be seperated using clone 17-3-4-1 for IP.
View the datasheet for more information and publications.
HAVE YOU REGISTERED?
Join the ever-growing global Ximbio community. Register and receive updates about new reagents, institutes and new features being added to the website.
