Cancer Research Technology’s protein kinase D (PKD) inhibitor, CRT0066101, has recently been published upon by a group based at Stony Brook University. This paper, published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, used CRT0066101 to investigate whether PKD signalling plays a distinct role in normal human keratinocytes proliferation. The team discovered a divergence between mice models and human keratinocytes; pharmacological inhibition of PKD in human keratinocytes resulted in growth arrest whereas the opposite was observed in mice.
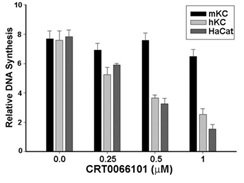
Relative DNA synthesis measured by [3H]thymidine incorporation in subconfluent cultures of human and mouse keratinocytes treated with increasing concentrations of CRT0066101. Image published in Ryvkin et al. 2015. J Biol Chem. 290(17):11199-208.
CRT0066101 is a specific inhibitor of all PKD isoforms. Christopher Ireson’s team at the Cancer Research Technology Discovery Laboratories developed CRT0066101 and showed that using the pancreatic cancer model, Panc-1, CRT0066101 could reduce BrdU incorporation, increase apoptosis and attenuate PKD activation. Furthermore Ireson’s team showed for the first time in 2008 that this inhibitor was orally bioavailable and blocked tumour growth in vivo.
Since CRT0066101’s creation in 2010, it has been extensively published upon. Positive effects have been observed in a wide range of cancers outside of pancreatic cancer including colorectal cancer, glioblastoma multiforme and chronic myelogenous leukemia.
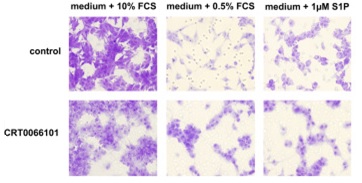
Interference with PKD2 expression reduces chemotactic migration and the invasive potential of U87MG cells Cells were treated with 1µM CRT0066101. Image published in Bernhart et al. 2013. Exp Cell Res. 319(13):2037-48.
Christopher Ireson has devoted his career to cancer pharmacology; discovering and developing new cancer chemotherapeutic agents at Sterix Ltd, Gray Cancer Institute, Apoxis and Cancer Research Technology amongst others. Ireson is now a Project Development Manager at Cancer Research Technology.
View the datasheet for more information and publications.
HAVE YOU REGISTERED?
Join the ever-growing global Ximbio community. Register and receive updates about new reagents, institutes and new features being added to the website.
